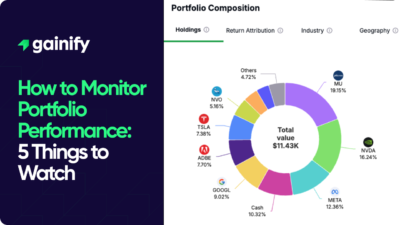
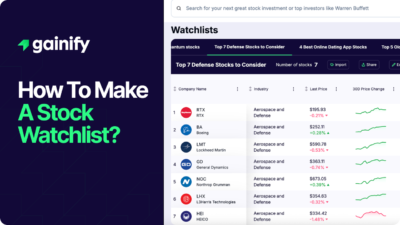
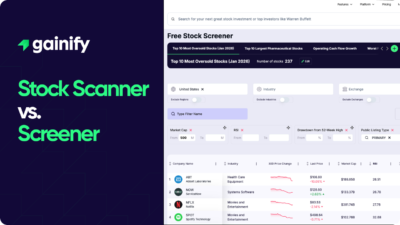
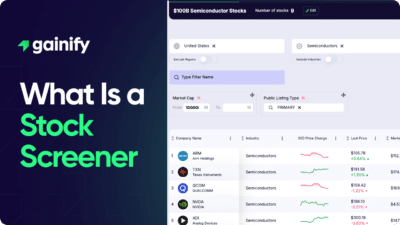
Earnings Yield Explained (2026): Definition, Formula, Interpretation, and Investment Use
Earnings yield measures how much profit a company generates relative to its share price. It expresses earnings as a percentage of price, making it the…