The best ESG stocks to consider in 2026 tend to be companies that appear repeatedly across major U.S. and global ESG indices. This consistency is not driven by perfect sustainability profiles, but by a combination of scale, governance quality, disclosure standards, and the ability to manage environmental and social risks over time.
In practice, ESG investing is less about selecting companies with the highest scores and more about understanding how ESG risks are identified, managed, and mitigated. Large, systemically important businesses often dominate ESG benchmarks because they have the resources to invest in sustainability initiatives, the governance structures to oversee them, and the reporting discipline required by index methodologies.
The ten ESG stocks discussed in this article are frequently included in ESG-focused portfolios because they strike a balance between business relevance and ESG risk management. They operate in complex industries, face real environmental and social challenges, and yet demonstrate measurable progress and transparency that index providers and institutional investors tend to favor.
ESG risk ratings produced by MorningStar Sustainalytics provide a structured way to assess how exposed a company is to material environmental, social, and governance risks, and how effectively those risks are managed. However, these ratings are best interpreted in context. Industry characteristics, execution capability, and the credibility of disclosures all play an important role in explaining why certain companies continue to appear across ESG frameworks year after year.
This perspective helps explain what ESG investing looks like in practice in 2026, and why a relatively consistent group of large-cap companies continues to anchor many ESG strategies.
What ESG Means and How It Is Used in Investing
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. In investing, it is a framework used to evaluate non-financial risks and practices that can materially affect a company’s long-term performance, resilience, and cost of capital.
Rather than measuring values or intent, ESG analysis focuses on how a company operates, how it manages risks beyond traditional financial metrics, and how those risks could be reflected in future cash flows, regulation, reputation, or operational stability.
Environmental (E)
The environmental pillar looks at how a company interacts with the natural environment and manages climate-related and resource-related risks. This includes factors such as:
- Greenhouse gas emissions and energy efficiency
- Exposure to climate regulation and carbon pricing
- Resource use, waste management, and supply chain emissions
- Physical risks from climate change, such as extreme weather
Environmental analysis is not about whether a company is “green” in absolute terms, but whether environmental factors create material risks or costs for its business model and whether those risks are actively managed.
Social (S)
The social pillar evaluates how a company manages relationships with employees, customers, suppliers, and society more broadly. Key areas include:
- Labor practices, safety, and employee retention
- Data privacy, product safety, and customer trust
- Supply chain standards and human rights risks
- Access, affordability, and societal impact of products or services
Social issues often translate into operational disruptions, legal exposure, or brand damage if not handled properly, making them financially relevant even when they appear non-financial at first glance.
Governance (G)
Governance focuses on how a company is run and how decisions are made. It is often considered the most critical ESG pillar because weak governance can amplify both environmental and social risks. Governance factors include:
- Board independence and oversight
- Executive compensation and incentive alignment
- Shareholder rights and transparency
- Business ethics, compliance, and risk controls
Strong governance increases the likelihood that environmental and social risks are identified early and addressed effectively.

How the Top 10 ESG Stocks for 2026 Were Selected
The selection of the top 10 ESG stocks for 2026 is based on a risk-focused and evidence-driven approach, rather than a simple ranking of sustainability scores. The goal is to identify companies that consistently appear across ESG indices because they manage material ESG risks effectively at scale.
The selection process considers four core dimensions:
- Sustainalytics ESG Risk Ratings: Sustainalytics assesses how exposed a company is to material environmental, social, and governance risks and how well those risks are managed. Lower unmanaged risk scores indicate stronger ESG risk control, adjusted for industry-specific factors.
- Market relevance and scale: companies included are large, systemically important businesses whose operations, supply chains, and capital allocation decisions have meaningful real-world impact. Scale matters because it affects both ESG risk exposure and the ability to invest in mitigation.
- Evidence from sustainability and environmental reporting: company disclosures are reviewed to assess whether stated ESG goals are supported by concrete actions, capital investment, governance oversight, and measurable progress over time. Emphasis is placed on execution rather than ambition.
- Consistency with institutional ESG index methodologies: the companies selected tend to appear repeatedly across major U.S. and global ESG indices. This reflects alignment with widely used index rules that prioritize industry-relative performance, controversy screening, and risk-adjusted ESG integration.
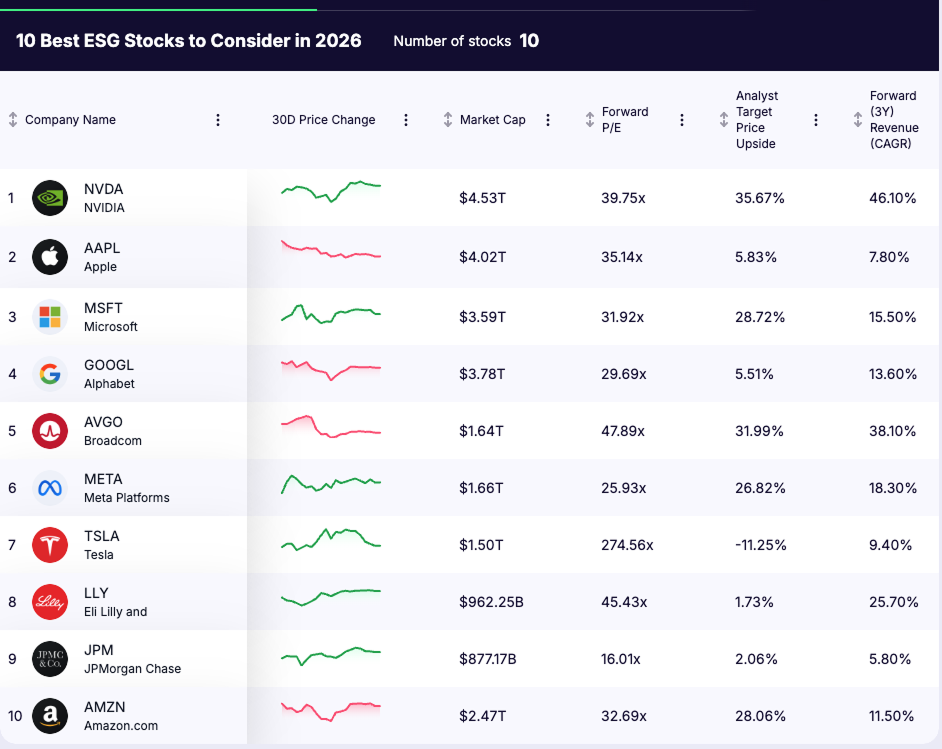
Taken together, these criteria produce a list of companies that are widely recognized as ESG leaders in terms of risk management and transparency, not as flawless or impact-perfect organizations. This list is intended to illustrate how ESG assessment works in practice and should not be interpreted as investment advice or a recommendation to buy or sell any security.
Top 10 ESG Stocks for 2026
1. NVIDIA (NASDAQ: NVDA)
ESG Risk Rating (Sustainalytics): Low Risk
Total ESG Risk Score: 12.4
- Environmental: 3.5
- Social: 4.1
- Governance: 4.9
Why NVIDIA Screens Well on ESG
NVIDIA operates in an energy-intensive industry, but its ESG profile reflects strong management of material risks rather than low exposure. Sustainalytics assigns NVIDIA a low risk score due to active mitigation of environmental, social, and governance challenges.
Key ESG Actions
- 100% renewable electricity for owned offices and data centers
- SBTi-validated targets:
- –50% Scope 1 & 2 emissions by FY2030
- –75% Scope 3 use-phase emissions intensity per PFLOP by FY2030
- Supplier engagement covering 80%+ of Scope 3 Category 1 emissions
- Major improvements in AI hardware energy efficiency
Key Takeaway
NVIDIA’s low ESG risk score reflects disciplined risk management and governance, which explains its consistent inclusion across major ESG indices.
2. Apple (NASDAQ: AAPL)
ESG Risk Rating (Sustainalytics): Low Risk
Total ESG Risk Score: 17.0
- Environmental: 6.8
- Social: 6.2
- Governance: 4.0
Why Apple Screens Well on ESG
Apple’s ESG profile reflects systematic risk reduction across its entire value chain, particularly in climate, materials, and supplier governance. Its score is driven not by low exposure, but by long-term execution against clearly defined environmental and social risks.
Key ESG Actions
- 100% renewable electricity across all corporate facilities since 2018
- Apple 2030 goal: carbon neutrality across Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions
- >60% reduction in total gross emissions since 2015 while revenue grew >65%
- 24% of materials shipped in 2024 sourced from recycled or renewable inputs
- 99% recycled rare earth elements used in all product magnets
- Supplier clean energy program covering 17.8 GW of renewable capacity
- Carbon-neutral products launched (e.g., Mac mini, Apple Watch lines)
Key Takeaway
Apple’s low ESG risk score reflects scale, discipline, and consistency, not headline initiatives. Its ability to decarbonize a complex global supply chain while maintaining profitability explains its persistent inclusion across nearly all major U.S. and global ESG indices.
3. Alphabet (NASDAQ: GOOGL)
ESG Risk Rating (Sustainalytics): Low Risk
Total ESG Risk Score: 11.8
- Environmental: 4.0
- Social: 3.9
- Governance: 3.9
Why Alphabet Screens Well on ESG
Alphabet operates one of the world’s largest data center and cloud infrastructures, making energy consumption its most material ESG risk. Sustainalytics assigns Alphabet a low ESG risk rating because these risks are actively managed through long-term clean energy procurement, efficiency improvements, and strong governance oversight.
Key ESG Actions
- 100% renewable energy matching for global operations since 2017
- Data center energy emissions reduced by 12% in 2024 despite a 27% increase in electricity demand
- Eight gigawatts of new clean energy contracts signed in 2024, the largest annual total in company history
- Industry-leading data center efficiency, with an average power usage effectiveness of approximately 1.1
- Progress toward 24/7 carbon-free energy, reaching 66% of global operations
Key Takeaway
Alphabet’s low ESG risk score reflects disciplined execution in managing energy and climate risks associated with AI and cloud growth. Its ability to scale computing infrastructure while improving efficiency and transparency explains its consistent inclusion across major U.S. and global ESG indices.
4. Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT)
ESG Risk Rating (Sustainalytics): Low Risk
Total ESG Risk Score: 13.1
- Environmental: 4.6
- Social: 4.2
- Governance: 4.3
Why Microsoft Screens Well on ESG
Microsoft operates large-scale cloud and AI infrastructure, which creates material environmental exposure. Sustainalytics rates Microsoft as low ESG risk because the company has embedded sustainability into governance, capital allocation, and long-term operational planning rather than treating it as a separate initiative.
Key ESG Actions
- Public commitment to become carbon negative, water positive, and zero waste by 2030
- Scope 1 and 2 emissions reduced 29.9% from the 2020 baseline by fiscal year 2024
- 34 gigawatts of contracted carbon-free electricity across 24 countries
- Nearly 22 million metric tons of carbon removal contracted through long-term agreements
- Over 90% reuse and recycling rate for cloud hardware servers and components
Key Takeaway
Microsoft’s ESG profile is driven by execution and transparency at scale. Its low ESG risk score reflects strong governance, measurable progress toward long-term climate targets, and disciplined management of AI-driven growth risks, supporting its inclusion across major global ESG indices.
5. Amazon.com (NASDAQ: AMZN)
ESG Risk Rating (Sustainalytics): Medium Risk
Total ESG Risk Score: 27.1
- Environmental: 13.2
- Social: 8.4
- Governance: 5.5
Why Amazon Screens Well on ESG
Amazon operates one of the world’s most complex and carbon-intensive business models, spanning global logistics, cloud infrastructure, and retail. Its ESG profile reflects high exposure but improving risk management, particularly in energy, transportation, and supply-chain oversight.
Key ESG Actions
- 100 percent of global electricity matched with renewable energy since 2023
- Net-zero carbon commitment across operations by 2040 under The Climate Pledge
- Over 31,000 electric delivery vehicles deployed globally as of 2024
- Global AWS data center efficiency with a Power Usage Effectiveness of 1.15
- Supplier decarbonization programs covering the majority of Scope 3 emissions
Key Takeaway
Amazon’s ESG score reflects scale-related risks, but also sustained investment in decarbonization, logistics efficiency, and supplier engagement. This balance explains its inclusion in most major U.S. and global ESG indices despite a higher absolute emissions footprint.
6. Meta Platforms (NASDAQ: META)
ESG Risk Rating (Sustainalytics): Low Risk
Total ESG Risk Score: 14.3
- Environmental: 4.8
- Social: 5.2
- Governance: 4.3
Why Meta Screens Well on ESG
Meta operates one of the world’s largest data center footprints, but its ESG profile reflects strong mitigation of environmental and social risks through energy sourcing, supplier engagement, and governance oversight.
Key ESG Actions
- Net zero operations since 2020 with 100% renewable electricity matched globally
- Over 15 gigawatts of wind and solar capacity added to global grids
- Target to reach net zero across the full value chain by 2030
- 48% of suppliers by emissions contribution have science-aligned targets
- Water-positive goal by 2030, with more than 1.6 billion gallons restored in 2024 alone
Key Takeaway
Meta’s low ESG risk score reflects disciplined management of energy, water, and supply-chain risks at hyperscale. Its continued inclusion in major ESG indices is driven by execution and transparency rather than low-impact operations.
7. Broadcom (NASDAQ: AVGO)
ESG Risk Rating (Sustainalytics): Medium Risk
Total ESG Risk Score: 18.1
- Environmental: 7.4
- Social: 5.6
- Governance: 5.1
Why Broadcom Screens Well on ESG
Broadcom operates in a resource-intensive semiconductor industry, but Sustainalytics views its ESG profile as manageable due to structured governance, strong operational controls, and steady progress on emissions and supply-chain oversight. Its score reflects moderate exposure with improving risk management, rather than low inherent impact.
Key ESG Actions
- 27% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 emissions versus 2021 baseline
- 61% of total electricity consumption from renewable sources
- Supplier climate engagement covering more than 79% of supplier spend
- ISO 14001 environmental management systems across major facilities
- Board-level oversight of ESG through a dedicated governance structure
Key Takeaway
Broadcom’s ESG profile is defined by disciplined execution rather than headline ambition. While environmental exposure remains material due to manufacturing and energy use, consistent emissions reductions, supplier engagement, and strong governance explain its inclusion in many institutional ESG indices despite a higher baseline footprint.
8. Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA)
ESG Risk Rating (Sustainalytics): Medium Risk
Total ESG Risk Score: 24.6
- Environmental: 5.1
- Social: 12.8
- Governance: 6.7
Why Tesla Screens Well on ESG
Tesla’s ESG profile is shaped by a clear contrast between product-level environmental benefits and company-level social and governance risks. Sustainalytics assigns a medium risk rating because, while Tesla’s products support decarbonization, operational, labor, and governance factors remain material.
Key ESG Actions
- Zero-emission vehicle portfolio supporting global transport decarbonization
- Energy generation and storage products contributing to grid resilience
- Vertical integration improving control over battery sourcing and manufacturing
- Public reporting on lifecycle emissions and battery recycling processes
- Investments in lithium refining and closed-loop battery materials
Key Takeaway
Tesla’s ESG score reflects that mission alone does not offset execution and governance risk. Its continued presence in ESG indices is driven by the environmental impact of its products, but its medium risk rating highlights the importance of social practices and governance discipline in long-term ESG assessment.
9. Eli Lilly and Company (NYSE: LLY)
ESG Risk Rating (Sustainalytics): Low Risk
Total ESG Risk Score: 14.8
- Environmental: 4.9
- Social: 5.6
- Governance: 4.3
Why Eli Lilly Screens Well on ESG
Eli Lilly operates in a highly regulated, resource-intensive pharmaceutical industry, yet Sustainalytics assigns a low ESG risk rating due to strong governance, mature compliance systems, and active management of environmental and access-to-health risks.
Key ESG Actions
- Scope 1 and 2 emissions reduced 37% from 2020 to 2024
- 58% of purchased electricity sourced from renewables in 2024
- Target to achieve carbon-neutral operations by 2030
- 100% of manufacturing sites meeting pharmaceutical environmental discharge standards
- Programs expanding global access to medicines in resource-limited regions
Key Takeaway
Eli Lilly’s ESG profile reflects disciplined execution rather than low exposure. Its low risk score is driven by strong governance, environmental controls across manufacturing, and sustained focus on patient access, supporting its inclusion in major U.S. and global ESG indices.
10. JPMorgan Chase & Co. (NYSE: JPM)
ESG Risk Rating (Sustainalytics): Medium Risk
Total ESG Risk Score: 22.6
- Environmental: 8.9
- Social: 7.1
- Governance: 6.6
Why JPMorgan Screens Well on ESG
As a global systemically important bank, JPMorgan Chase has high exposure to environmental and social risks through its lending, investing, and capital markets activities. Its ESG profile reflects strong risk management and governance rather than low underlying exposure, which supports its inclusion in most major ESG indices.
Sustainalytics assigns JPMorgan a medium ESG risk rating due to its scale and exposure to carbon-intensive sectors, partially offset by robust compliance systems, transparent climate risk frameworks, and board-level oversight.
Key ESG Actions
- Commitment to mobilize 2.5 trillion dollars toward sustainable development initiatives by 2030
- Portfolio-level emissions targets across high-emitting sectors
- 100% renewable electricity for global operations
- Climate risk integrated into credit, market, and operational risk processes
- Strong governance, regulatory compliance, and financial crime controls
Key Takeaway
JPMorgan Chase’s ESG standing is driven by disciplined governance and risk controls at scale. While environmental exposure remains material, its transparency and management systems explain its consistent presence across major U.S. and global ESG indices.
ESG Stocks for 2026
Company | Ticker | ESG Risk Rating | Overall Score | Environmental | Social | Governance |
NVIDIA | NVDA | Low Risk | 12.4 | 3.5 | 4.1 | 4.9 |
Apple | AAPL | Low Risk | 17.0 | 6.8 | 6.2 | 4.0 |
Alphabet | GOOGL | Low Risk | 11.8 | 4.0 | 3.9 | 3.9 |
Microsoft | MSFT | Low Risk | 13.1 | 4.6 | 4.2 | 4.3 |
Amazon.com | AMZN | Medium Risk | 27.1 | 13.2 | 8.4 | 5.5 |
Meta Platforms | META | Low Risk | 14.3 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 4.3 |
Broadcom | AVGO | Medium Risk | 18.1 | 7.4 | 5.6 | 5.1 |
Tesla | TSLA | Medium Risk | 28.1 | 10.6 | 11.2 | 6.3 |
Eli Lilly and Company | LLY | Low Risk | 14.8 | 4.9 | 5.6 | 4.3 |
JPMorgan Chase & Co. | JPM | Medium Risk | 22.6 | 8.9 | 7.1 | 6.6 |
How Sustainalytics ESG Risk Ratings Work
ESG data used by many financial platforms and institutional investors is produced by Sustainalytics, one of the most established ESG research providers globally. Its methodology is designed to measure financially material ESG risk, not ethical alignment, values, or corporate intentions.
At its core, the Sustainalytics framework asks a practical investment question:
How exposed is a company to material ESG risks, and how effectively are those risks managed?
The outcome is a Total ESG Risk Score, which represents the level of unmanaged ESG risk remaining after a company’s policies, controls, and governance practices are taken into account.
What the ESG Risk Score Represents
- Lower scores indicate lower unmanaged ESG risk
- The score reflects risk to enterprise value, not sustainability ambition
- Commitments and targets matter only if supported by governance, execution, and controls
- The focus is on downside risk, not positive impact or values alignment
This approach explains why companies operating in high-impact industries can still score well if their risks are actively and consistently managed.
ESG Risk Score Categories
Sustainalytics classifies companies into five risk bands:
- Negligible Risk: 0–10
- Low Risk: 10–20
- Medium Risk: 20–30
- High Risk: 30–40
- Severe Risk: 40 and above
These categories allow investors to compare ESG risk across companies and industries using a standardized scale.
Environmental, Social, and Governance Subscores
Each company’s total score is built from three underlying components:
- Environmental risk, covering issues such as energy use, greenhouse gas emissions, resource management, and exposure to climate regulation
- Social risk, including labor practices, employee safety, product responsibility, data privacy, and customer impact
- Governance risk, assessing board oversight, executive compensation, shareholder rights, and business ethics
Crucially, these subscores are weighted by industry materiality. A software company, a pharmaceutical manufacturer, and a global bank are evaluated against different ESG risk profiles based on where material risks realistically arise.
What ESG Scores Do and Do Not Measure
It is important to understand what Sustainalytics ratings are designed to capture:
- ESG scores do not reward ambition, pledges, or long-term promises
- They penalize weak controls, repeated controversies, and unmanaged exposure
- A company can publish strong sustainability goals and still score poorly if execution or governance is weak
- Conversely, a company with high inherent ESG exposure can score well if risk management is strong
This risk-based framework explains why ESG indices tend to include large, complex companies with robust governance and disclosure systems. Inclusion is driven by risk management quality, not by the absence of impact or controversy.
Understanding this methodology is essential when interpreting ESG ratings and comparing companies across sectors, especially in the context of long-term, risk-aware investing.
What This ESG List Really Shows
Looking across these ten companies, several consistent patterns become clear:
- ESG leaders are often large, complex businesses, not niche or low-impact firms. Scale increases ESG exposure, but it also provides the resources and governance needed to manage that exposure effectively.
- Low ESG risk is driven by management quality, not by the absence of environmental or social impact. Strong controls, oversight, and disclosure matter more than operating in a “clean” industry.
- Environmental performance alone is not sufficient. Companies with strong climate strategies can still score poorly if social practices or governance structures are weak.
- Social and governance factors increasingly drive ESG outcomes, especially in technology, finance, healthcare, and consumer-facing platforms where data, labor, and oversight risks are material.
Taken together, this reinforces a key point: in 2026, ESG investing functions primarily as a risk assessment framework, not a values-based ranking of companies.
Final Perspective: ESG as a Long-Term Risk Framework
The best ESG stocks for 2026 are not defined by perfection. They are companies that identify material risks early, disclose them clearly, and commit capital and governance resources to managing those risks over time.
Sustainalytics ESG risk ratings provide a structured way to compare how companies handle non-financial risks that increasingly influence financial outcomes, including:
- Cost of capital, through regulatory, legal, and reputational exposure
- Regulatory and compliance risk, particularly in climate, data, and labor
- Brand and customer trust, which affects pricing power and demand stability
- Long-term shareholder value, by reducing the likelihood of severe downside events
When used properly, ESG analysis does not replace traditional financial analysis. It adds context, highlights risks that may not yet be reflected in earnings or valuation, and helps investors better understand the durability of a business model over time.
Disclaimer
This content is provided for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice, a recommendation, or an offer to buy or sell any security. ESG ratings are based on third-party methodologies and publicly available information, which may change as new data becomes available. All investments involve risk, including the potential loss of capital. Investors should conduct their own research and consider professional advice before making investment decisions.




