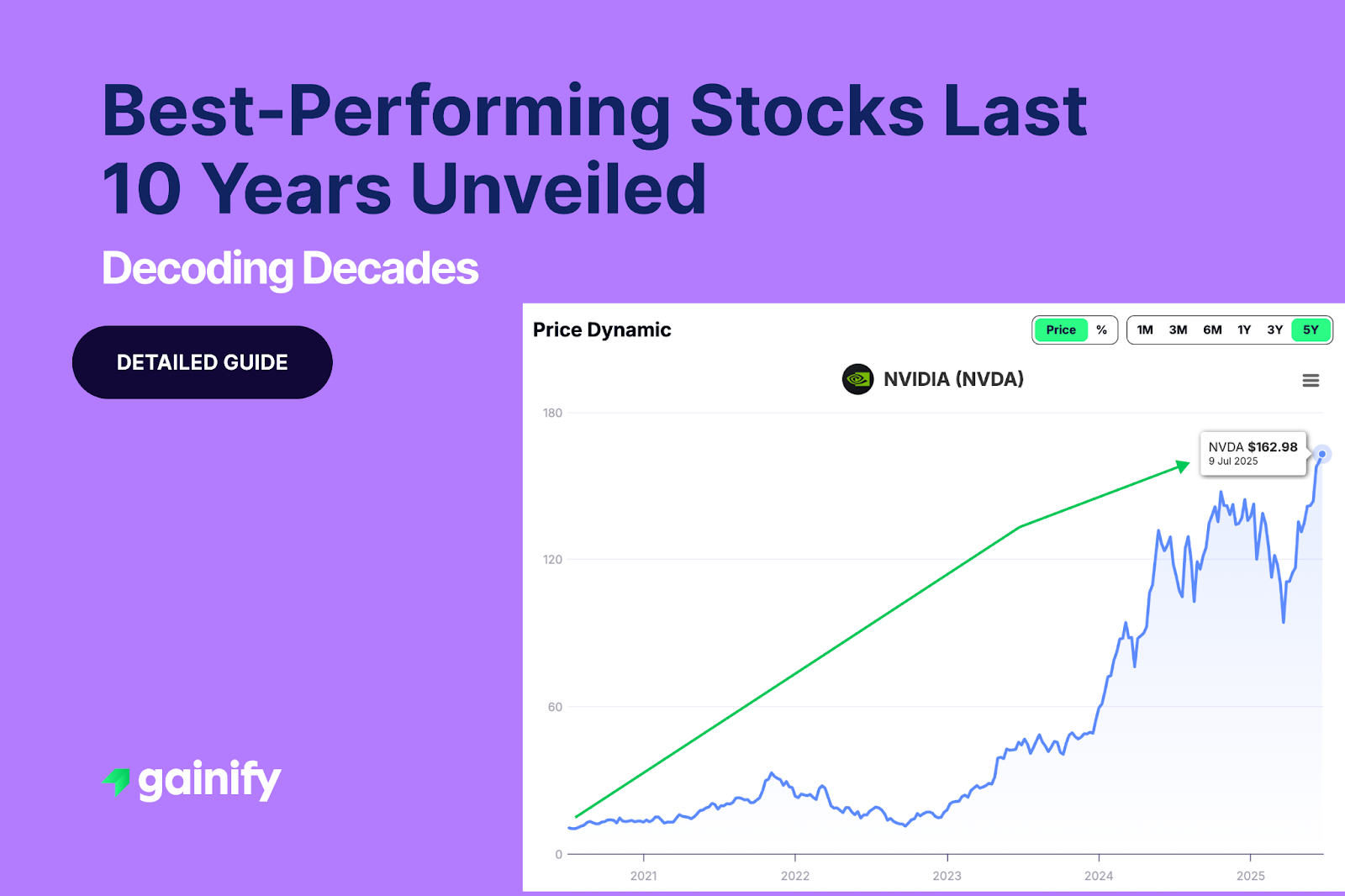
The electric vehicle (EV) transition in 2026 is entering a new phase of growth. As EV adoption continues to expand, attention is increasingly focused on scale, cost efficiency, energy density, and how batteries connect vehicles to the wider energy system. At the center of this shift is the EV battery.
Batteries are now the core economic driver of electric vehicles. They represent a large share of vehicle cost, directly affect range and performance, and shape how EV platforms compete. Beyond transportation, battery manufacturing plays a growing role in grid scale energy storage, industrial power systems, and national energy strategies. These overlapping uses are changing how value is created across both the automotive and energy markets.
For investors, this points toward battery producers and battery technology leaders rather than vehicle makers alone. These companies supply multiple automakers, serve both EV and energy storage markets, and benefit from long term demand that is less dependent on short term vehicle sales cycles.
Several structural trends support this outlook. Global electrification continues to accelerate across transportation. Energy storage capacity is expanding to support renewable power and grid stability. Battery technology continues to improve, lowering costs while increasing performance. At the same time, governments are pushing for more localized and resilient battery supply chains.
Together, these forces create a compelling investment profile. Leading battery companies tend to have strong customer relationships, long term supply contracts, and positions within EV platforms that become harder to replace as production scales.
Against this backdrop,seven EV battery stocks stand out heading into 2026: CATL, BYD, LG Energy Solution, Panasonic Holdings, Samsung SDI, QuantumScape, and Tesla. Together, they offer diversified exposure to large scale battery manufacturing, advanced battery technology, and integrated energy platforms.
Key Takeaways
- EV battery economics now determine competitiveness: battery cost per kilowatt hour, energy density, cycle life, and safety directly impact EV pricing, margins, and adoption. As batteries become the largest cost and performance driver, pricing power is shifting toward battery manufacturers with scale and advanced technology.
- EV battery demand extends beyond vehicles: battery makers are benefiting from growth in grid scale energy storage, renewable power integration, and industrial electrification. This expands the EV battery market beyond cars and supports more durable, multi cycle demand.
- Battery suppliers hold critical positions in the EV ecosystem: leading EV battery companies provide essential components, manufacturing expertise, and proprietary battery technology. These capabilities are deeply embedded in automaker and utility platforms, creating high switching costs and long term competitive advantages.
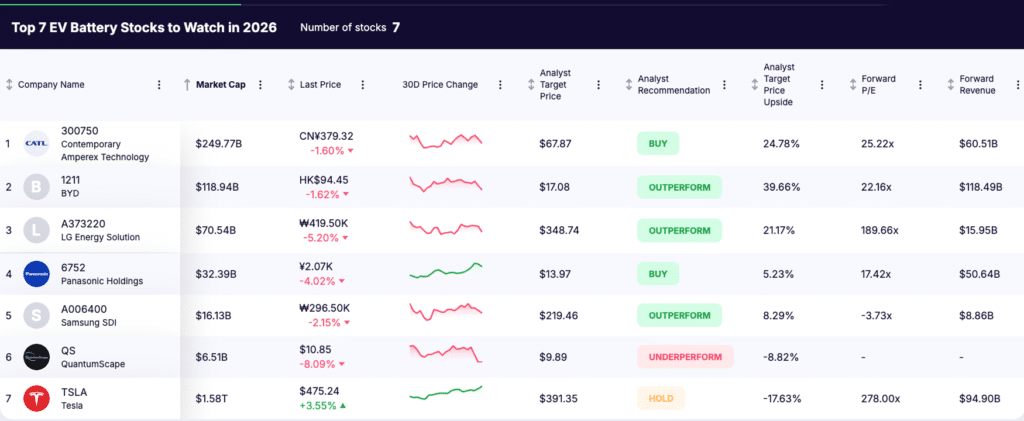
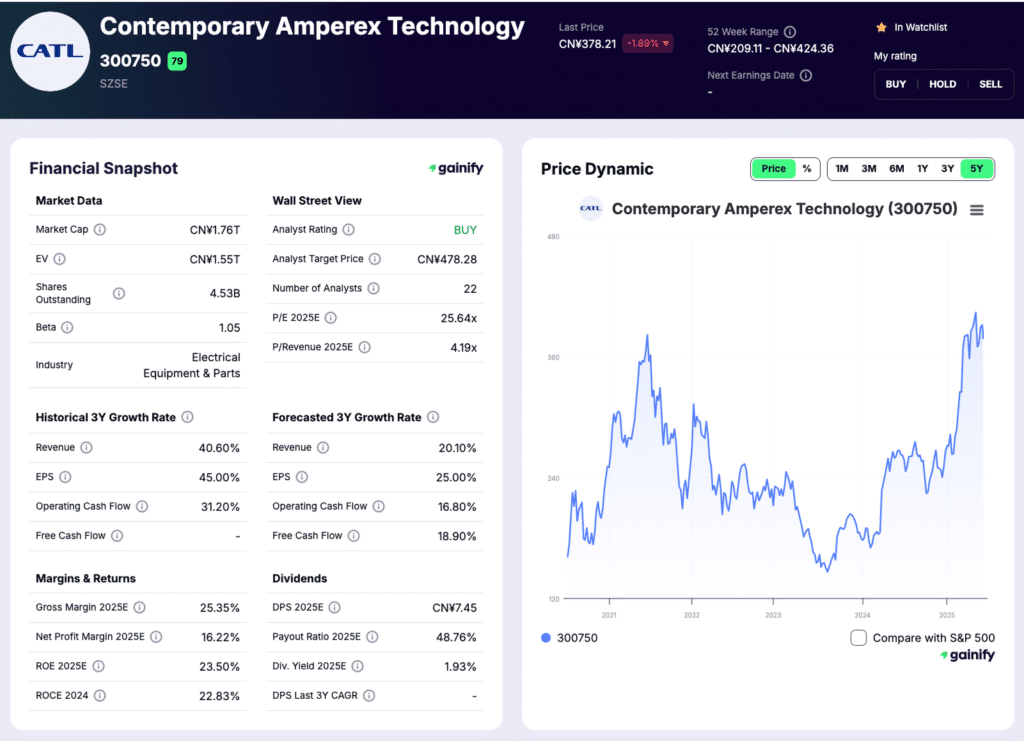
1. Contemporary Amperex Technology (SZSE: 300750)
Market Cap: $249.8B
Industry Role: Global EV and energy storage battery leader
Analyst Rating: Buy
Forward P/E: 25.22x
CATL is the backbone of the global EV battery supply chain. As the world’s largest producer of lithium-ion batteries, the company supplies a wide range of automakers across China, Europe, and increasingly other global markets. Its scale advantage is unmatched, allowing CATL to drive down costs while continuing to invest heavily in next-generation chemistries and manufacturing processes.
CATL benefits from diversification across both EV batteries and energy storage systems. While EV demand can fluctuate by region and policy cycle, grid-scale storage continues to expand as renewable penetration increases. This dual exposure reinforces revenue stability and strengthens CATL’s strategic relevance to governments and utilities as well as automakers.
During the most recent reporting period, the company generated RMB 178.9 billion in revenue, representing a 7.3 percent year over year increase, while net cash generated from operating activities reached RMB 58.7 billion, up more than 31 percent from the prior year. This strong cash generation reflects high capacity utilization, disciplined cost control, and growing demand across both transportation and energy storage applications
Investment Thesis: CATL represents the closest thing to a core infrastructure asset within the EV ecosystem. Its scale, customer entrenchment, and cost leadership position it to compound earnings as electrification deepens globally.
Key Risk: Geopolitical and trade tensions could limit market access or increase regulatory friction outside China.
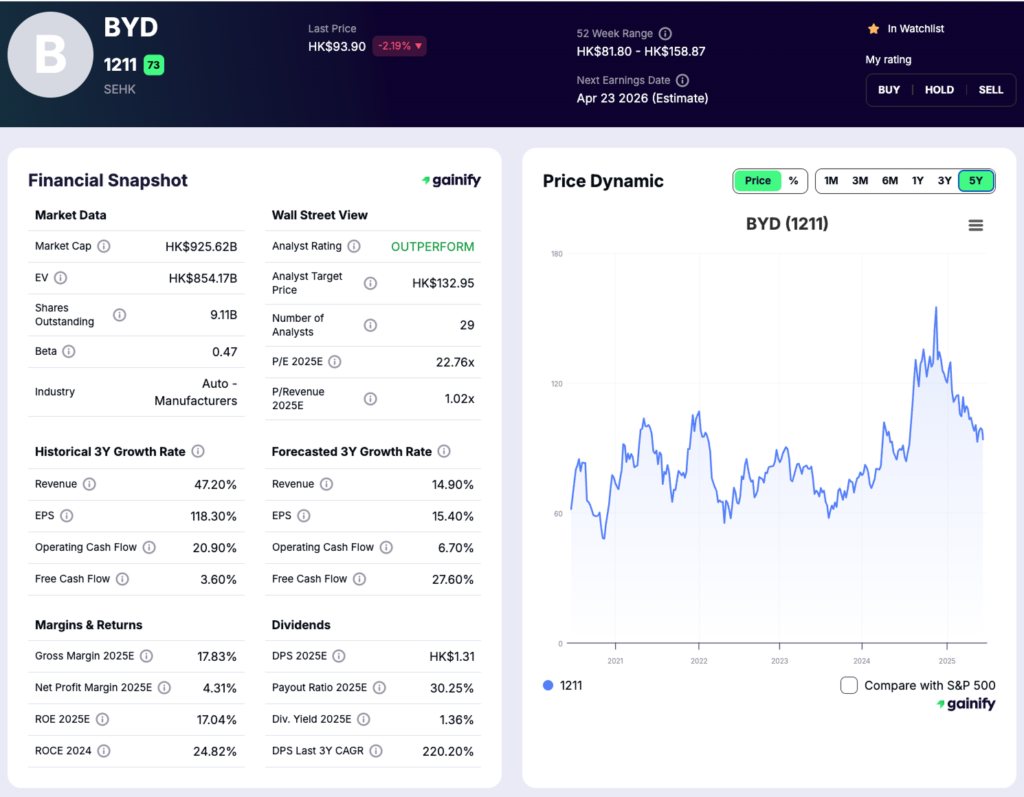
2. BYD Company (SEHK: 1211)
Market Cap: $118.9B
Industry Role: EV batteries, vehicles, and energy storage
Analyst Rating: Outperform
Forward P/E: 22.16x
BYD is one of the most vertically integrated players in the global EV battery ecosystem, combining large scale battery manufacturing with electric vehicle production and energy storage solutions. The company is a leading producer of rechargeable batteries and has built deep internal capabilities across battery design, materials, and system integration. Its Blade Battery platform has become a core differentiator, emphasizing safety, durability, and cost efficiency across both passenger and commercial vehicle applications.
BYD benefits from diversification across EV batteries, vehicles, and energy storage systems. While vehicle demand can fluctuate by market and pricing conditions, battery and energy storage demand continues to expand as electrification and grid stabilization accelerate globally. This integrated model supports volume growth, reinforces cost control, and strengthens BYD’s strategic relevance across transportation and energy markets.
During the most recent reporting period, BYD generated RMB 371.3 billion in revenue, representing a 23.3 percent year over year increase, while profit attributable to shareholders reached RMB 15.5 billion, up 13.8 percent from the prior year. The company also invested RMB 30.9 billion in research and development, reflecting a sustained commitment to battery technology, safety innovation, and manufacturing efficiency .
Investment Thesis: BYD offers a rare combination of battery scale, vertical integration, and technology ownership. Its ability to design, manufacture, and deploy batteries across multiple end markets positions the company to compound value as EV adoption and energy storage deployment continue to expand.
Key Risk: Competitive pricing pressure in the global EV market and capital intensity across manufacturing operations could weigh on margins during periods of aggressive volume growth.
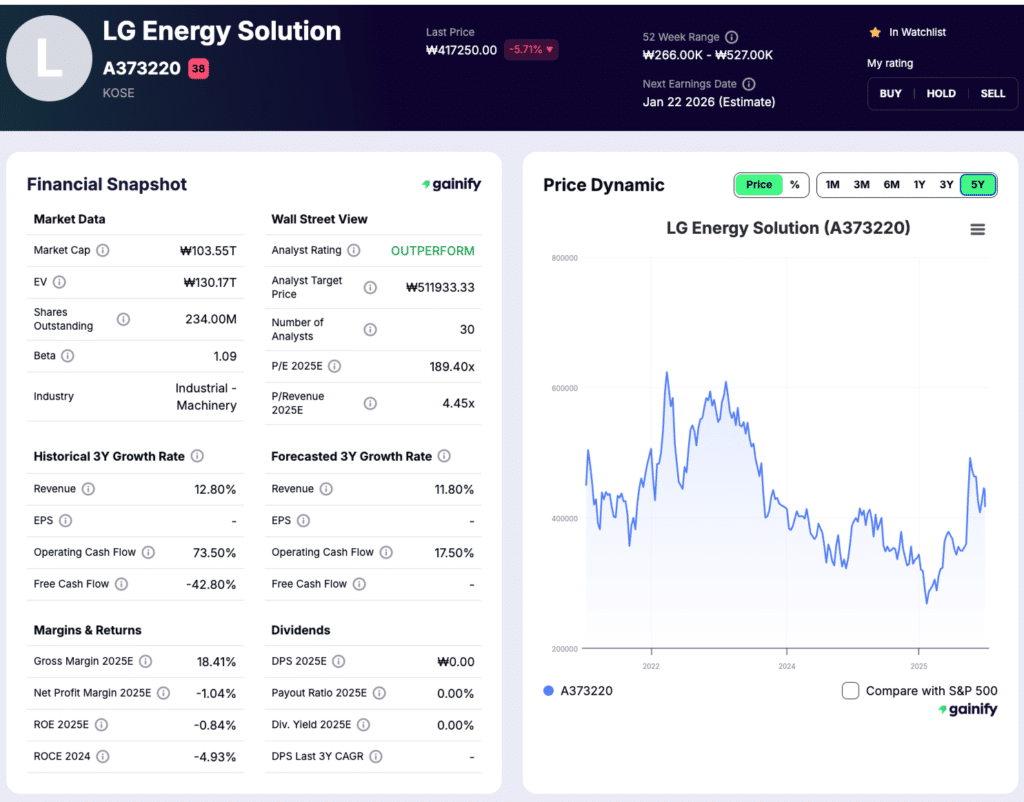
3. LG Energy Solution (KOSE: A373220)
Market Cap: $70.5B
Industry Role: EV and energy storage battery manufacturing
Analyst Rating: Outperform
Forward P/E: 189.7x
LG Energy Solution is one of the largest dedicated EV battery manufacturers globally and a core supplier to automakers across North America, Europe, and Asia. The company produces lithium ion batteries for electric vehicles and energy storage systems, with capabilities spanning multiple cell formats and chemistries. Its role as a long term supplier to Western OEMs positions it at the center of efforts to localize battery supply chains and secure multi year production capacity.
LG Energy Solution benefits from exposure to both EV batteries and energy storage systems. While near term EV demand can fluctuate by region and model cycle, demand for stationary energy storage continues to grow as utilities expand grid scale capacity to support renewable power generation. This diversification supports long term volume growth and reinforces LG Energy Solution’s strategic importance within the global electrification value chain.
During the most recent reporting period, LG Energy Solution generated KRW 3.05 trillion in revenue, while operating profit declined to a loss of KRW 591 billion as pricing pressure, customer inventory adjustments, and lower utilization weighed on near term margins. Despite this, the company ended the period with KRW 2.15 trillion in cash and cash equivalents, providing financial flexibility to continue investing in capacity expansion and technology development.
Investment Thesis: LG Energy Solution represents a scale driven, long duration investment in global EV battery adoption. Its deep integration with Western automakers, expanding exposure to energy storage, and strong liquidity position it to benefit as utilization rates recover and industry conditions normalize.
Key Risk: High fixed manufacturing costs and ongoing pricing pressure could continue to impact profitability if EV demand recovery is slower than expected.
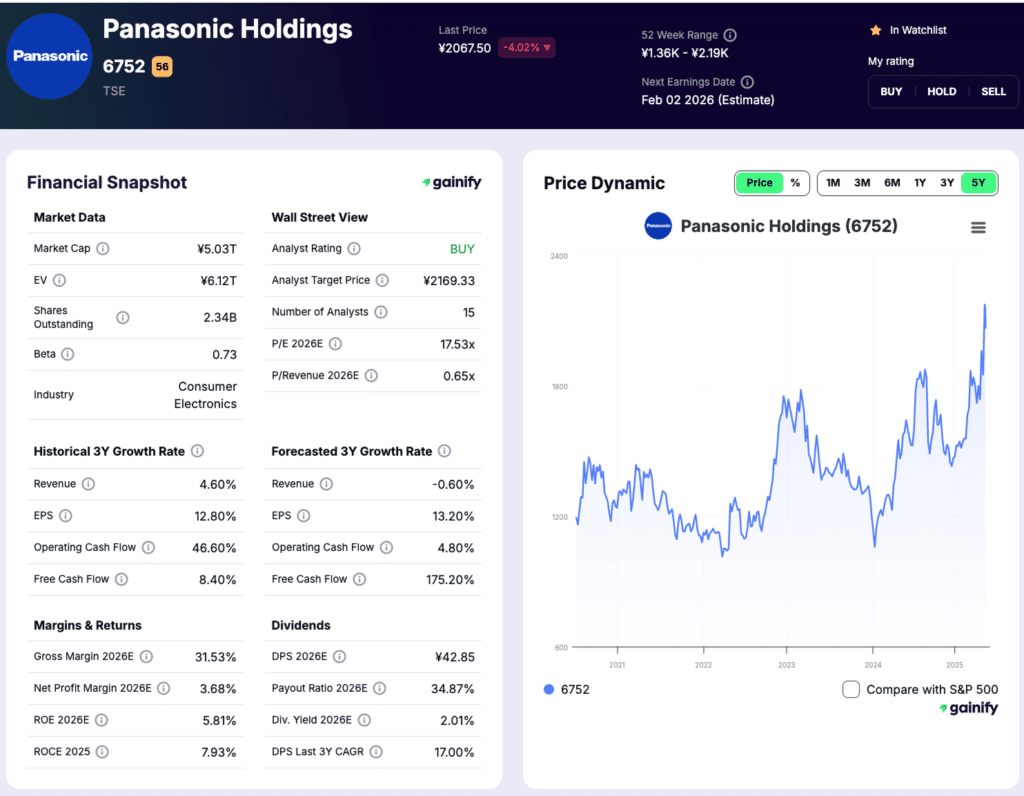
4. Panasonic Holdings (TSE: 6752)
Market Cap: $32.4B
Industry Role: Advanced battery cells and industrial electronics
Analyst Rating: Buy
Forward P/E: 1.47x
Panasonic Holdings is a long standing leader in advanced battery manufacturing and one of the most established suppliers of high performance lithium ion batteries for electric vehicles. The company’s battery operations are concentrated within its Energy segment, which produces cylindrical cells used in EV platforms and energy storage applications. Panasonic’s technical expertise, manufacturing discipline, and long operating history position it as a trusted supplier in performance sensitive EV segments.
Rather than relying on a single growth engine, Panasonic operates across multiple end markets, including EV batteries, industrial energy solutions, and broader electronics businesses. This structure provides insulation during periods of uneven EV demand and allows the company to continue funding battery development even when automotive volumes soften. Energy remains a strategic pillar as electrification and power efficiency trends extend well beyond passenger vehicles.
During fiscal 2026 second quarter, Panasonic generated ¥1.92 trillion in consolidated sales, while adjusted operating profit totaled ¥90.4 billion. Within the Energy segment, sales reached ¥227.6 billion, though adjusted operating profit declined to ¥1.1 billion as lower automotive battery volumes and pricing adjustments weighed on near term performance. Despite this pressure, Panasonic reported EBITDA of ¥182.3 billion, underscoring the company’s ability to generate operating cash flow across its diversified business base
Investment Thesis: Panasonic offers exposure to EV battery technology through a disciplined, engineering driven manufacturer with deep customer relationships and proven production capability. Its conservative balance sheet, diversified earnings base, and focus on high performance battery segments position it to benefit as EV demand and utilization recover.
Key Risk: Near term profitability in the Energy segment remains sensitive to EV production volumes and pricing dynamics, which could delay margin recovery if automotive demand remains uneven.
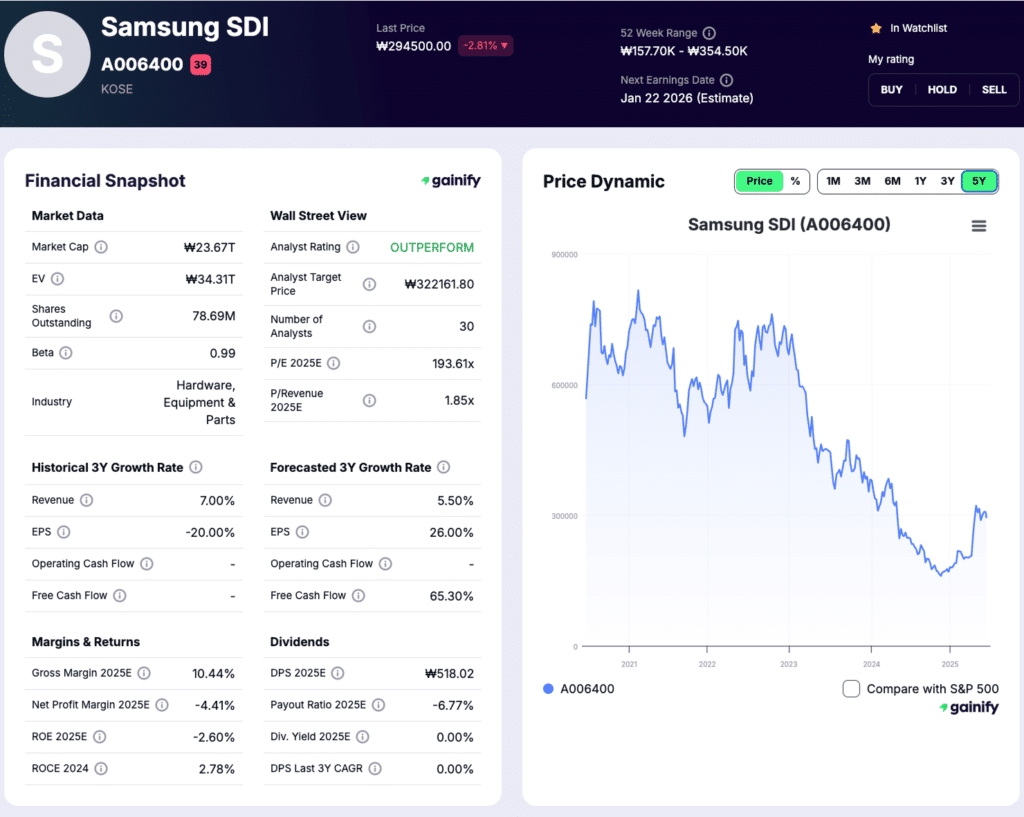
5. Samsung SDI (KOSE: A006400)
Market Cap: $16.1B
Industry Role: Premium EV and ESS batteries
Analyst Rating: Outperform
Forward P/E: Negative
Samsung SDI occupies a premium position within the EV battery market, with a strategic focus on high performance batteries for electric vehicles and energy storage systems. Rather than pursuing maximum volume, the company emphasizes quality, safety, and energy density, supplying batteries to automakers and industrial customers that prioritize reliability and long cycle life. This positioning places Samsung SDI closer to the higher end of the battery value curve.
The company operates across two main businesses, batteries and electronic materials, with batteries representing the core long term growth driver. While EV demand has softened in some regions, Samsung SDI continues to invest in next generation battery platforms and capacity upgrades, aiming to align production with future demand rather than short term market fluctuations. Energy storage applications also remain an important offset, supporting demand outside passenger vehicle cycles.
In the most recent quarter, Samsung SDI reported KRW 3.05 trillion in revenue, down from prior year levels, while operating income declined to a loss of KRW 591 billion as lower utilization and pricing pressure weighed on profitability. Despite these headwinds, the company ended the period with KRW 2.15 trillion in cash and cash equivalents, providing balance sheet strength to sustain investment through the downturn and position for recovery when volumes improve
Investment Thesis: Samsung SDI offers exposure to the premium end of the EV battery market, where technical requirements and customer switching costs are higher. Its focus on quality driven applications, combined with a strong balance sheet, positions the company to benefit as EV demand stabilizes and utilization rates recover.
Key Risk: Near term earnings remain sensitive to EV production volumes and fixed cost absorption, and prolonged weakness in global EV demand could delay a return to profitability.
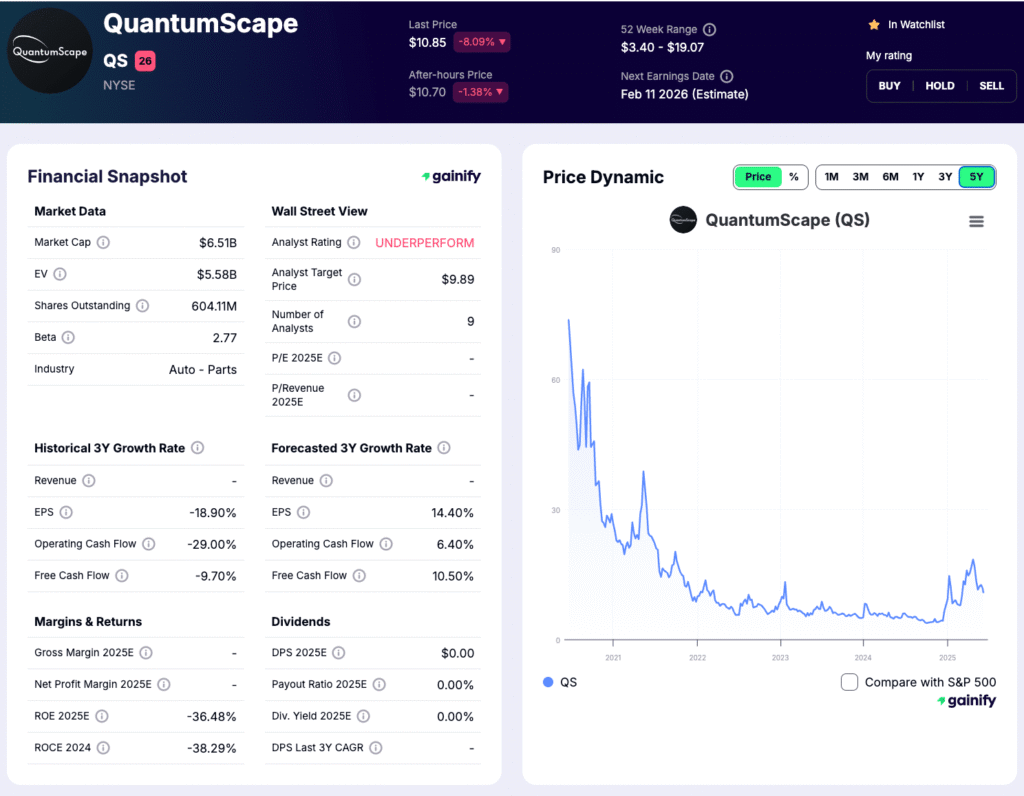
6. QuantumScape (NYSE: QS)
Market Cap: $6.5B
Industry Role: Solid-state battery technology
Analyst Rating: Underperform
Forward P/E: Negative
QuantumScape sits at the most speculative end of the EV battery landscape, and its stock chart reflects that reality. The company is focused on developing solid state lithium metal batteries that promise higher energy density, faster charging, and improved safety compared with conventional lithium ion cells. Unlike scaled manufacturers, QuantumScape is still in the technology validation phase, with value tied to future breakthroughs rather than current production.
The stock’s long term price trajectory highlights the market’s reassessment of timing and risk. Shares have declined sharply from early cycle highs and now trade closer to the lower end of their multi year range, signaling investor caution around commercialization timelines and capital intensity. At the same time, recent rebounds within a wide trading range suggest ongoing interest from investors willing to speculate on successful technical milestones rather than near term revenue.
From an operational standpoint, QuantumScape remains pre revenue, with cash usage driven primarily by research, engineering, and pilot manufacturing development. The company continues to fund progress through its balance sheet while advancing cell testing and manufacturing readiness. This places the stock firmly in the category of long duration optionality rather than traditional growth or value investing.
Investment Thesis: QuantumScape represents a high risk, high potential bet on next generation battery technology. If solid state batteries achieve scalable commercial viability, the payoff could be significant given the central role batteries play in EV economics. The current share price reflects skepticism, but also embeds optional upside tied to successful execution.
Key Risk: The chart underscores the primary risk. Commercialization remains uncertain, timelines may extend, and further capital raises could dilute shareholders. Without clear progress toward scalable production, the stock is likely to remain volatile and sentiment driven.
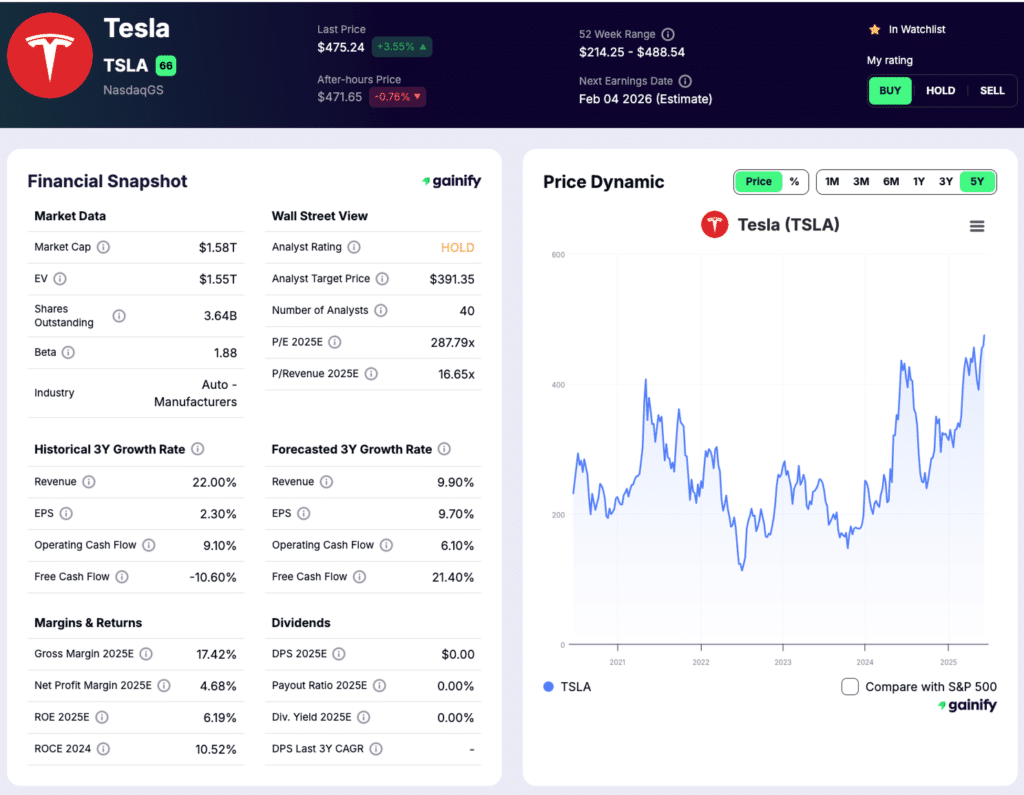
7. Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA)
Market Cap: $1.58T
Industry Role: EVs, batteries, and energy storage platforms
Analyst Rating: Hold
Forward P/E: 278x
Tesla treats batteries as a strategic platform capability rather than a single component sourced from one channel. While the company is often described as vertically integrated, its battery model is deliberately hybrid. Tesla both produces batteries internally and sources large volumes of battery cells from external suppliers, allowing it to balance cost, scale, and geographic flexibility across vehicles and energy storage systems.
Internally, Tesla is developing and manufacturing its proprietary 4680 battery cells at facilities in the United States. These cells are designed to reduce cost per kilowatt hour, simplify manufacturing, and enable tighter integration between the battery and vehicle structure. Production of 4680 cells has progressed beyond the pilot stage, but internal output still represents a minority share of Tesla’s total battery volume.
At the same time, Tesla continues to rely heavily on established partners for most of its battery cells. Panasonic remains a key supplier for cylindrical lithium ion cells, particularly in North America. CATL supplies lithium iron phosphate batteries for standard range vehicles, especially in China and Europe. LG Energy Solution provides additional lithium ion cells for certain vehicle configurations. Even when cells are externally sourced, Tesla typically designs and assembles its own battery packs, control software, and thermal management systems.
This hybrid model supports Tesla’s EV-first strategy while enabling growth in stationary energy storage. Battery capacity can be allocated between vehicles and grid scale applications depending on demand, capital returns, and market conditions, improving overall utilization of manufacturing assets.
Investment Thesis: Tesla offers exposure to electric vehicles supported by a flexible battery strategy that balances in house development with supplier scale. By keeping batteries closely tied to EV design and manufacturing, Tesla maintains control over costs and performance while reducing dependency risk as battery technology continues to evolve.
Key Risk: Tesla remains dependent on external suppliers for most battery cells. Delays in scaling internal production, supplier pricing pressure, or slower EV demand growth could weigh on margins and limit the benefits of deeper battery integration.
Industry Outlook for 2026 and Beyond
The EV battery industry is entering a phase defined by execution, efficiency, and scale optimization rather than pure capacity expansion. As large manufacturing footprints are established globally, the focus is shifting toward improving utilization rates, reducing cost per kilowatt hour, and tailoring battery chemistries to specific applications across vehicles and energy storage.
Structural demand remains strong. Global EV battery demand is projected to grow at a compound annual rate of roughly 20 percent through the end of the decade, driven by rising electric vehicle adoption and expanding energy storage requirements. By 2030, total annual battery demand is expected to exceed 3 terawatt hours, up from well under 1 terawatt hour just a few years ago. This growth reflects both higher vehicle penetration and larger battery packs per vehicle, as well as increasing deployment of stationary storage systems.
Grid scale energy storage is emerging as a major incremental driver. Industry estimates project global energy storage installations to grow at more than 25 percent annually, as power systems add batteries to stabilize grids, support renewable generation, and manage peak demand. This creates a second long duration demand channel that is not directly tied to vehicle sales cycles.
Policy continues to shape the industry’s trajectory. Government incentives and localization programs in the United States, Europe, and Asia are accelerating investment in domestic battery manufacturing and supply chains. These policies support sustained capital spending while reducing reliance on single-region production hubs. At the same time, ongoing improvements in battery chemistry, safety, and manufacturing processes are steadily lowering costs and expanding addressable use cases.
Near term volatility is likely to persist, particularly around pricing, inventory levels, and capacity utilization. However, batteries have become a foundational component of both electric transportation and modern energy infrastructure. This strategic importance supports continued investment, long term demand visibility, and a multi cycle growth outlook extending well beyond 2026.
Conclusion
EV battery stocks offer direct exposure to one of the most important industrial transformations of the coming decade. Rather than relying on the success of individual vehicle models or short term shifts in consumer demand, leading battery companies participate across the entire electrification ecosystem, supplying automakers, utilities, and energy infrastructure providers.
As the industry continues to scale, companies with manufacturing leadership, technological depth, and diversified end markets are positioned to deliver more durable earnings profiles than EV manufacturers alone. Batteries sit at the intersection of transportation and energy, giving suppliers long duration relevance as electrification expands.
Looking toward 2026 and beyond, battery focused businesses remain central to the electrification investment thesis. Their role as essential enablers of electric vehicles and modern energy systems supports sustained demand, ongoing investment, and long term value creation across market cycles.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. All investments involve risk, including potential loss of capital. Investors should conduct their own research and consult a qualified financial professional before making investment decisions.