Is bitcoin worth investing for investors searching for the next frontier of value, much like gold once was in earlier eras of financial discovery? Throughout history, investors have gravitated toward assets that challenge existing systems and redefine how wealth is stored and transferred. Bitcoin (BTC) began as a niche technological concept but has since emerged onto the global stage, igniting debate over whether it represents a modern form of digital gold, a new monetary alternative, or a fundamentally transformative asset for the financial system.
Bitcoin’s journey has been anything but conventional. Its genesis in 2009, born from an anonymous creator known as Satoshi Nakamoto and rooted in a decentralized digital ledger, defied traditional financial structures. Early adopters saw its promise of independence from central banks and governments, a truly global and permissionless digital currency. Over the years, it has demonstrated astonishing volatility, experiencing meteoric rises that captured headlines, followed by precipitous corrections that tested the resolve of even the most ardent believers. This rollercoaster ride is a defining characteristic of the asset, shaping perceptions and fueling both fervent optimism and deep skepticism.
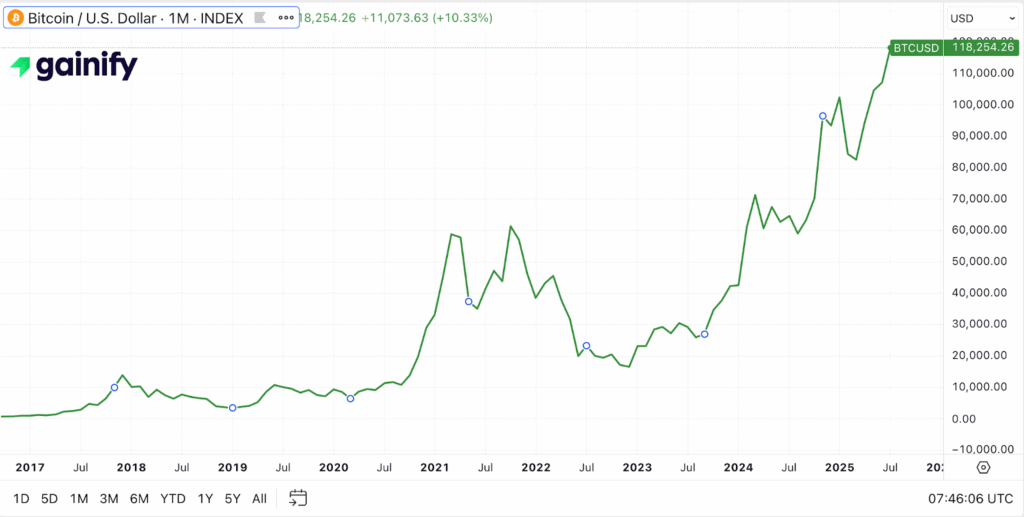
The conversation around Bitcoin investing has matured meaningfully. After reaching a new all-time high of over $120,000 USD, with its market cap exceeding $2.3 triWhile volatility remains a defining feature, recent price action reflects a market supported by deeper liquidity, broader ownership, and more established infrastructure than in prior cycles.
A seasoned financial professional understands the allure of groundbreaking assets and the vital importance of a balanced perspective. Bitcoin represents a fascinating intersection of technology, economics, and human behavior. It is a digital asset unlike any other, offering both compelling opportunities and considerable challenges. This guide aims to navigate the intricate landscape of Bitcoin, dissecting its potential, illuminating its risks, and helping in an investment decision for those considering this digital frontier.
The Allure of Bitcoin: Why Investors Take Notice
Bitcoin’s appeal stems from several core characteristics that differentiate it from traditional assets:
- Decentralization: Unlike government-issued fiat currencies, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network. No single entity controls it. This feature attracts those seeking independence from centralized financial systems.
- Scarcity: Bitcoin’s supply is capped at 21 million coins. This hard limit, enshrined in its code and detailed in its original whitepaper by Satoshi Nakamoto, creates inherent scarcity. This often leads to its comparison with precious metals like gold as a potential “digital gold” and inflation hedge. This fixed supply contrasts sharply with fiat currencies, which can be printed in unlimited quantities.
- Halving Events: Approximately every four years, the reward Bitcoin miners receive for adding new blocks to the Bitcoin blockchain is cut in half. The most recent Bitcoin halving occurred in April 2024. Historically, these events have reduced the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation, impacting supply dynamics and often preceding significant price increases in the subsequent months or year. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results.
- Technological Foundation: Bitcoin is built on blockchain technology, a secure and transparent distributed ledger. This underlying technology, utilizing cryptographic techniques, enables secure peer-to-peer transactions. While Bitcoin pioneered blockchain, much of the recent innovation in the broader blockchain space like smart contracts and decentralized finance (DeFi) happens on other platforms. Bitcoin’s own core innovation pace is intentionally conservative, focusing on its role as a secure, decentralized digital value transfer system.
- Accessibility: The widespread availability of user-friendly crypto exchange platforms and, more recently, spot Bitcoin ETFs has dramatically increased accessibility for both retail and institutional investors. One can now gain exposure through familiar investment vehicles, simplifying the process of stock purchases that reflect Bitcoin’s exchange rate. For example, BlackRock’s IBIT ETF has become one of the fastest ETFs in history to reach significant assets under management.
Institutional Acceptance: A New Era for Bitcoin
A pivotal shift in the narrative around Bitcoin’s legitimacy has been its surging institutional acceptance, particularly since the approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in early 2024. This development has transformed how major financial players view and interact with the digital currency.
BlackRock’s Leadership
BlackRock, one of the world’s largest asset managers, launched the iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT), a spot Bitcoin ETF. The fund quickly became one of the fastest-growing ETFs in history, reaching billions in assets under management within months. As of 2026, IBIT holds several hundred thousand Bitcoin, reflecting significant inflows from both institutional and retail investors seeking exposure through regulated channels. The scale and pace of its growth highlight a material shift in how traditional financial institutions allocate capital to digital assets.
Fidelity’s Strong Presence
Fidelity, through its Fidelity Digital Assets division, introduced the Fidelity Wise Origin Bitcoin Fund (FBTC), another spot Bitcoin ETF that has attracted substantial investor interest. Alongside BlackRock, Fidelity has been instrumental in bringing legitimacy and infrastructure to Bitcoin investing. These firms, together with others like Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley offering related services, are building the institutional backbone that appeals to asset owners such as pension funds, endowments, and family offices.
Widespread ETF Adoption
Beyond the largest players, several other asset managers have launched spot Bitcoin ETFs, including Bitwise (BITB), ARK 21Shares (ARKB), and VanEck (HODL). In mid-2025, the collective assets under management across all US-listed spot Bitcoin ETFs have reached record highs, with total holdings absorbing a significant share of newly mined Bitcoin. This consistent demand supports the view of Bitcoin as a maturing asset class, increasingly used for portfolio diversification across a range of investor profiles.
Flows from Traditional Clients
Inflows into spot Bitcoin ETFs are being driven by a wide spectrum of institutional wealth. Financial advisors are now incorporating Bitcoin into client strategies using these vehicles, while many family offices and select sovereign wealth funds are actively allocating capital to spot Bitcoin exposure. These inflows are addressing long-standing concerns about regulatory clarity and custody, making Bitcoin more accessible within traditional investment frameworks compared to earlier futures-based ETFs.
Corporate Treasury Adoption
In addition to asset managers, some public companies continue to hold Bitcoin on their balance sheets as part of their treasury strategy. While this trend began with tech firms like MicroStrategy and Tesla, new participants, including Trump Media & Technology Group, have expressed interest in digital assets as part of broader reserve diversification efforts. This signals growing acceptance of Bitcoin as a treasury reserve asset amid continued macroeconomic uncertainty.
The sustained wave of institutional adoption has added significant liquidity to the Bitcoin market, validated its position within mainstream finance, and supported its role as a viable long-term holding across a broad set of investor types.
Potential Benefits: Why Bitcoin Could Be a Smart Move
For those with a high tolerance for risk and a long-term investment horizon, Bitcoin offers several compelling potential benefits, as highlighted by leading experts:
- Diversification: Bitcoin’s price movements do not always perfectly correlate with traditional asset classes like the S&P 500. Adding Bitcoin to an investment portfolio could potentially offer investment diversification benefits, though its volatility means this comes with significant risk.
- Inflation Hedge: While once debated, the argument for Bitcoin as a robust inflation hedge is gaining traction among experts, particularly given its finite supply and recent performance against currency fluctuations. Some corporations are increasingly adding Bitcoin to their treasury reserves, viewing it as a superior alternative to traditional stores of value.
- Asymmetric Return Potential: Given its relatively young age as an asset class and its potential for broader adoption, many experts see Bitcoin as offering “asymmetric” return potential. This means the upside could be significantly larger than the downside, even considering the risk of substantial loss. Price targets from major financial institutions for 2026 and beyond reflect this optimism.
- Evolving Regulatory Clarity: While regulation remains a key risk, there is a clear global trend toward developing clearer frameworks for digital currency. In the US, for instance legislative proposals like the Digital Asset Market Clarity Act are advancing to establish clearer rules for stablecoins and digital assets, with a notable shift towards “pro-crypto” sentiment. This push for clearer rules is attracting more conservative capital, providing regulatory tailwinds.
- Geopolitical Resilience: Surprisingly to some, Bitcoin has demonstrated increasing resilience amid geopolitical tensions. Recent global conflicts showed Bitcoin’s market structure holding firm, supported by institutional investments that saw dips as buying opportunities. This suggests a maturing role for Bitcoin during periods of uncertainty, akin to “digital gold.” Argentina’s President Javier Milei, for example, has expressed strong pro-Bitcoin sentiments, viewing it as a tool against government overreach
The Other Side of the Coin: Significant Risks and Concerns
Despite its potential, investing in Bitcoin comes with substantial risks that no investor should overlook. As an expert, I urge caution and a thorough understanding of these drawbacks:
- Extreme Price Volatility: Bitcoin continues to be highly volatile, with its price capable of shifting dramatically in short periods. These fluctuations are often driven by market sentiment, news events, macroeconomic shifts, regulatory announcements, or large trades by major holders. Such volatility can lead to significant financial losses if risk is not carefully managed. Even during periods of strong price performance, experts caution that volatility is likely to remain a core characteristic of the asset.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape: While regulatory clarity has improved in some regions, the global approach to cryptocurrency regulation is still developing. Future laws could influence Bitcoin’s legality, usage, taxation, and investment appeal. Regulatory bodies like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), and the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) continue to shape policy frameworks. Divergent approaches in jurisdictions like the U.S., European Union, and Asia contribute to ongoing uncertainty and complexity for investors.
- Lack of Intrinsic Value: Unlike stocks, which are backed by company assets and earnings, or bonds, which are supported by issuer obligations, Bitcoin is not tied to any physical asset or productive output. Its value is largely based on supply and demand, market perception, adoption trends, and investor sentiment. This characteristic is frequently cited by critics who question its long-term viability as an investment.
- Security Vulnerabilities: While the Bitcoin blockchain itself is considered secure, individual holdings remain susceptible to theft, hacking, phishing attacks, and loss of access due to forgotten credentials or misplaced wallets. Incidents like the Bybit security breach in 2025 and the historic Mt. Gox collapse highlight ongoing risks. Investors are responsible for securing their digital assets, often by using hardware (cold) wallets for long-term storage. Cybersecurity concerns remain higher in crypto than in traditional finance.
- Environmental Impact: Bitcoin mining consumes significant amounts of electricity, contributing to concerns about its environmental footprint. According to the Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index, Bitcoin’s annual energy use rivals that of mid-sized countries. Much of this energy still comes from fossil fuels, though efforts from groups like the Bitcoin Mining Council aim to increase the share of renewables. Despite some progress, Bitcoin’s environmental impact continues to attract scrutiny from policymakers and environmental advocates.
- Market Competition: Bitcoin is the most valuable cryptocurrency by market capitalization, but it competes with thousands of alternative digital assets. Some of these, like Ethereum (ETH), offer different functionalities such as smart contracts and decentralized applications. The rapid pace of innovation in the crypto sector means that newer platforms could challenge Bitcoin’s dominance in specific areas.
- “Digital Gold” Versus Payment Use Case: While Bitcoin is often described as “digital gold” and used as a store of value, its price volatility and relatively high transaction fees limit its effectiveness as a medium of exchange. Despite early visions of Bitcoin being used for everyday payments, its primary adoption remains concentrated in investment and wealth preservation use cases.
- Market Manipulation and Scams: The crypto market remains vulnerable to manipulation due to lower levels of oversight compared to traditional financial markets. Schemes such as pump-and-dump operations, rug pulls, and Ponzi schemes have been common in the space. Investors must perform thorough due diligence and remain vigilant.
- Consumer Protection Gaps: Unlike traditional financial products, cryptocurrencies are typically not covered by protections such as those offered by the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC) or the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). This means that in cases of fraud, exchange failure, or loss of funds, recourse options may be limited or nonexistent.
- Tax Implications: Cryptocurrency transactions are subject to taxation in many jurisdictions and often require meticulous tracking for reporting capital gains, losses, and income. Tax authorities such as the IRS treat cryptocurrencies as property, adding complexity for investors and requiring detailed record-keeping to remain compliant.
A Balanced View: Beyond the Hype and Skepticism
Leading voices in finance are approaching Bitcoin with a more nuanced perspective. Rather than making simple bullish or bearish claims, they are examining its role in markets, its long-term potential, and the responsibilities that come with investing in it.
- Maturation as an Asset Class: Bitcoin is increasingly seen as evolving into a more established asset. The introduction of spot Bitcoin ETFs has expanded access and improved liquidity. These developments have helped bring a broader investor base into the market. While volatility remains, many view these changes as steps toward more stable and structured participation.
- Part of a Diversified Portfolio: Some financial advisors now view a small allocation to Bitcoin as a reasonable option for investors with higher risk tolerance. Allocations are typically limited to a small percentage of the portfolio. This approach aims to capture potential upside while keeping exposure to volatility under control within an overall investment strategy.
- Focus on Long-Term Trends: Many analysts and investors prefer to focus on long-term patterns rather than daily or weekly price movements. Bitcoin halving cycles, sustained institutional interest, and ongoing regulatory developments are seen as key forces shaping its multi-year trajectory.
- Technological Foundation: Bitcoin’s blockchain continues to be recognized as an important innovation. It enables secure, decentralized transaction recording and has influenced the development of other digital finance systems. While Bitcoin is the most well-known application, the broader concept of distributed ledger technology remains a focus of investment and research.
- Prudent Risk Management: Experienced investors recommend a cautious and deliberate approach to Bitcoin exposure. This includes clearly defined investment goals, appropriate position sizing, and secure custody solutions. Many experts emphasize that capital invested in Bitcoin should be limited to amounts that investors can afford to lose without financial hardship.
This perspective reflects a growing effort to evaluate Bitcoin thoughtfully. Rather than relying on hype or fear, it encourages informed decision-making based on research, strategy, and awareness of the risks involved.
Understanding Bitcoin Through Key Concepts
To make informed investment decisions, it is important to understand several key concepts commonly associated with Bitcoin:
- Blockchain: The decentralized and tamper-resistant digital ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions. This technology ensures transparency, security, and traceability across the network.
- Mining: The process through which new Bitcoins are issued and transactions are verified. It requires substantial computational power to solve cryptographic puzzles and maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
- Bitcoin Halving: A pre-programmed event that occurs roughly every four years, reducing the block reward for miners by 50 percent. This slows the rate at which new Bitcoins enter circulation and influences supply-side dynamics.
- Volatility: A measure of how much the price of an asset fluctuates over time. Bitcoin is widely known for its high price volatility, often reacting to market sentiment, macroeconomic conditions, and regulatory news.
- Cold Storage and Hot Wallets: Methods for storing Bitcoin. Cold wallets store assets offline and offer higher security, while hot wallets are connected to the internet, making them more convenient for frequent transactions but more vulnerable to cyber threats.
- Spot Bitcoin ETFs: Exchange-traded funds that directly hold Bitcoin rather than derivatives. These ETFs allow investors to gain exposure to Bitcoin through traditional brokerage accounts without managing the underlying asset themselves. They have attracted large inflows from both retail and institutional investors.
- Inflation Hedge: An investment that is expected to preserve or grow in value during periods of rising inflation. Some investors view Bitcoin as a potential hedge against currency devaluation due to its limited supply.
- Market Capitalization: The total value of all Bitcoins in circulation, calculated by multiplying Bitcoin’s current price by the total number of coins mined. It is a commonly used metric to assess the scale of Bitcoin relative to other cryptocurrencies or asset classes.

Navigating the Digital Future
The question of “is Bitcoin worth investing in” does not have a simple yes or no answer. It is a nuanced investment decision that demands a deep understanding of its unique characteristics, its historical volatility, and the dynamic forces shaping its future. As we have explored, Bitcoin offers compelling potential benefits rooted in its decentralization and scarcity, alongside significant risks driven by regulatory uncertainty, security concerns, and its inherent price swings. Its recent surge to new all-time highs over $120,000 USD, fueled by unprecedented institutional adoption of Bitcoin, signals a maturing asset class with a trillion-dollar market cap.
Key Takeaways:
- Bitcoin is a highly volatile, speculative asset, but it is increasingly gaining legitimacy and institutional acceptance, reaching new all-time highs over $120,000 USD in mid-2025, before entering a consolidation phase around the $90,000 level.
- Its fixed supply and halving events are core to its appeal, with growing expert consensus on its potential as a long-term inflation hedge, often referred to as “digital gold.”
- The approval and massive inflows into spot Bitcoin ETFs, led by firms like BlackRock and Fidelity, have fundamentally reshaped its market, significantly increasing accessibility and institutional participation including interest from sovereign wealth funds.
- Key risks remain extreme price volatility and potential market manipulation, evolving regulatory frameworks that lack full regulatory protections, and significant environmental concerns regarding its energy consumption and water use.
- Super experts from institutions like Goldman Sachs and Moon Pursuit Capital emphasize that any allocation to Bitcoin should be a small, strategic component of a well-diversified investment portfolio, only for investors with a very high risk tolerance, and not as a replacement for traditional index funds.
- Thorough and independent research into the core technology, including Bitcoin’s blockchain and the Lightning Network, as well as the evolving regulatory landscape, such as cryptocurrency taxation and oversight by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), is essential before considering any investment in Bitcoin. This is especially important given recent security breaches and regulatory actions involving major exchanges in 2025.
Ultimately, deciding whether to include Bitcoin in your investment portfolio comes down to your individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and belief in its long-term transformative potential. Approach this digital frontier with a clear understanding of both its promises and its perils. The choice is clear: navigate with caution, invest with purpose.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bitcoin Investment
Q: Is Bitcoin considered a safe investment?
A: No, Bitcoin is widely considered a high-risk investment. Its price is highly volatile and can change significantly over short periods. While some investors have seen strong returns, the potential for large losses is equally real. It is not viewed as a safe asset like government bonds or insured bank deposits. According to research from the Pew Research Center published in late 2024, most Americans remain skeptical about the safety of investing in cryptocurrencies.
Q: How does the Bitcoin halving affect its price?
A: Bitcoin halving events occur approximately every four years and reduce the reward that miners receive for validating transactions. This slows the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation. Historically, halvings have often preceded periods of price increases, based on reduced supply and continued demand. However, many other factors influence price, and past patterns do not guarantee future performance.
Q: Can I lose all my money investing in Bitcoin?
A: Yes, there is a real possibility of losing a large portion—or even all—of your investment. Bitcoin’s volatility, ongoing regulatory uncertainty, and the risk of theft or loss through compromised wallets or exchange breaches all contribute to this risk. Incidents involving crypto scams, exchange failures, or market manipulation remain concerns. Only invest what you can afford to lose and always conduct proper due diligence.
Q: Is Bitcoin a good hedge against inflation?
A: Bitcoin’s potential as an inflation hedge is still debated. Supporters argue that its fixed supply makes it a strong candidate for preserving value in inflationary environments. Critics point to its short history, high volatility, and correlation with risk assets, especially during market downturns. While some institutions have begun to include Bitcoin in inflation-conscious strategies, it has not yet proven to be a consistently reliable inflation hedge like gold. The International Monetary Fund and other global bodies continue to study its evolving role in financial systems.
Q: How do institutional investors get involved in Bitcoin?
A: Institutional investors now primarily gain exposure to Bitcoin through spot Bitcoin ETFs, which began launching in early 2024 in key markets like the U.S. These products provide regulated access without requiring direct custody of the asset. Institutions also invest indirectly through companies that hold Bitcoin or by using specialized custodial services and over-the-counter trading platforms. Firms like BlackRock, Fidelity, and others have played a major role in accelerating institutional adoption.
Q: What is the role of regulation in Bitcoin’s future?
A: Regulation plays a critical role in shaping Bitcoin’s long-term outlook. In the United States, legislation such as the Digital Asset Market Clarity Act, under discussion, seeks to define clearer rules around crypto assets. Well-structured regulations can help increase transparency, reduce fraud, and attract more institutional capital. However, excessive or unclear regulation could limit access or suppress innovation. Regulatory bodies such as the SEC, FinCEN, and international financial authorities continue to shape the environment around Bitcoin and broader crypto markets.
Q: How can I research Bitcoin and other crypto investments?
A: Reliable research is essential before investing. For companies involved in the crypto space, the SEC’s EDGAR database provides access to public filings. For direct information on Bitcoin, use trusted sources such as regulated exchanges, blockchain analytics platforms, academic research, and financial news outlets. Reading a project’s original whitepaper is also recommended. Be cautious of hype-driven content and avoid investment opportunities that promise guaranteed returns. Remember, crypto assets are not insured by agencies like the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC) or the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC).




