Artificial Intelligence has moved from the lab into the marketplace, powering everything from AI assistants in our phones to full self-driving systems in cars. This new stage, often called AI 2.0, is transforming the economy. Companies are no longer just experimenting with machine learning and neural networks, but they are deploying these tools at scale, integrating them into core operations, and generating measurable revenue growth.
The AI revolution is supported by an expanding backbone of AI infrastructure: advanced GPU architecture, high-performance networking chips, and data center infrastructure designed for AI workloads. Cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud are enabling businesses of all sizes to tap into generative AI and Large Language Models without building their own costly data servers.
AI 2.0 stocks have become some of the most closely watched companies in the S&P 500 and Nasdaq Composite, with massive increases in market capitalization over the past two years. From semiconductor leaders like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing to platform giants like Microsoft and Alphabet, these firms are reshaping industries ranging from e-commerce to healthcare.
For investors, this is a structural shift in the global economy, not a passing tech theme. Understanding which companies build the compute, power, and connectivity behind AI helps you target opportunities with stronger risk adjusted returns.
What Makes AI 2.0 Different
AI 2.0 is not about hypothetical breakthroughs. It is about systems that work in production today, at scale, inside real businesses. The stack spans advanced integrated circuits, GPUs optimized for training and inference, and foundry services that produce custom silicon. Companies are building AI data centers with the speed, reliability, and security that enterprise software requires.
AI 2.0 has three core traits, plus four that are emerging as decisive.
- Monetization: Products and services that convert directly into sales, cost savings, or higher margins, tracked with clear financial KPIs.
- Scalability: Cloud services that process billions of daily transactions, with automation that keeps latency and unit cost under control as usage grows.
- Specialization: Solutions tuned for specific domains such as autonomous systems, biological data analysis, and creative workflows, which improves accuracy and adoption.
- Operational reliability: Enterprise buyers expect uptime, audit trails, and role based access. Observability, monitoring, and rollback plans are built into the deployment.
- Data governance and security: Clean pipelines, privacy controls, and policy compliance determine what can be shipped to customers, not only what can be built in a lab.
- Cost and energy efficiency: Procurement and placement of compute, plus model and hardware choices, drive cost per token and power per task. Efficiency wins repeat budgets.
- Integration with existing systems: AI 2.0 plugs into CRM, ERP, content management, and data warehouses, which shortens adoption cycles and raises switching costs.
What to look for as an investor: companies that pair technical capability with reliable delivery, measurable economics, and secure operations. Those are the ones most likely to compound value as adoption widens.
The 15 AI 2.0 Stocks to Watch in 2026
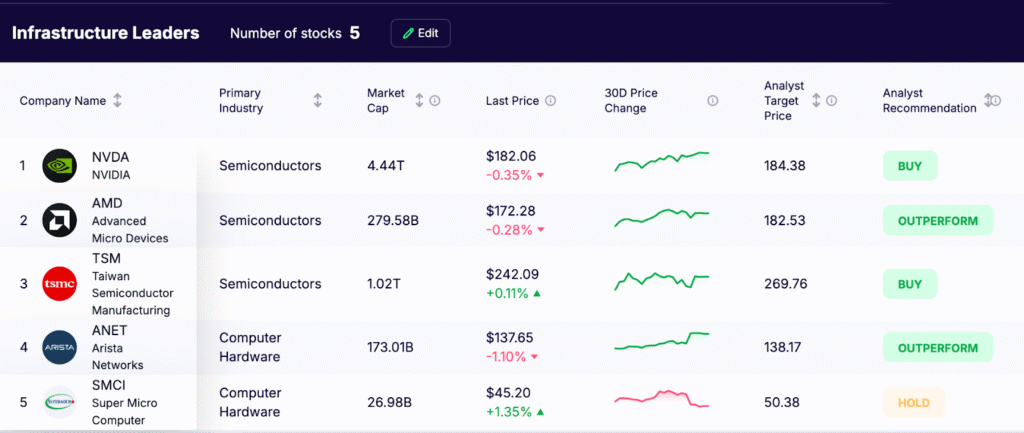
Infrastructure Leaders
These companies supply the hardware and backbone for AI workloads. They benefit directly from rising chip demand and the buildout of data center infrastructure.
- NVIDIA (NVDA) – Dominates AI computing with its Blackwell GPUs and Blackwell Architecture designed for large-scale neural networks.
- Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) – Competes with NVIDIA in AI-focused GPU architecture and custom chips for cloud workloads.
- Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing (TSM) – The world’s leading chip foundry providing foundry services for AI leaders.
- Arista Networks (ANET) – Specializes in networking chips that power modern AI data centers.
- Super Micro Computer (SMCI) – Builds high-performance data servers optimized for AI workloads.
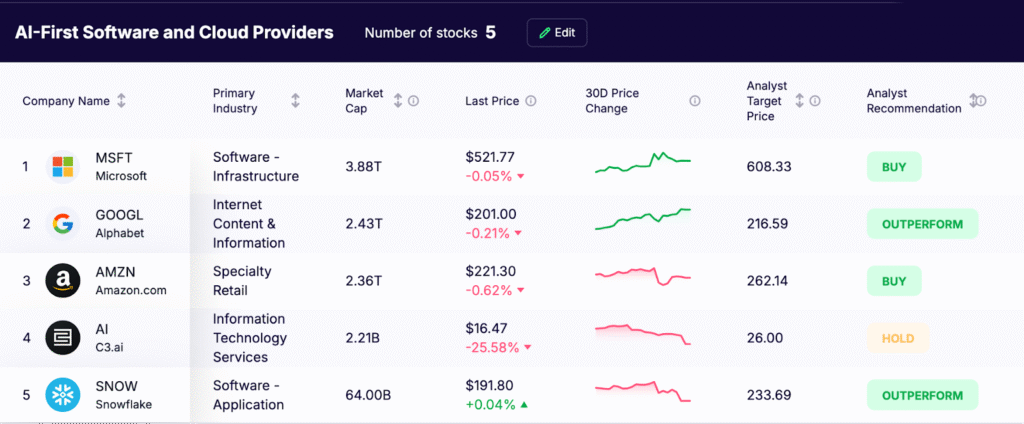
AI-First Software and Cloud Providers
These companies make AI tools accessible to enterprises, often via cloud services.
- Microsoft (MSFT): Integrates large language models across Azure AI and Microsoft 365 through Copilot. Offers tooling for developers, security teams, and business users to build and deploy assistants at scale.
- Alphabet (GOOGL): Expands Google Cloud with Vertex AI and Gemini for generative and agentic workflows. Provides MLOps, safety features, and data governance for enterprise adoption.
- Amazon (AMZN): Uses AWS for AI computing with NVIDIA GPUs and custom Trainium and Inferentia chips. Services like Bedrock and SageMaker help customers build, tune, and deploy models, while AI supports retail, logistics, and advertising.
- C3.ai (AI): Delivers an enterprise AI platform and prebuilt applications for sectors such as manufacturing, energy, financial services, and defense. Designed for regulated environments with access controls, audit trails, and monitoring.
- Snowflake (SNOW): The Data Cloud unifies data, governance, and compute in one place. With Snowpark and Cortex AI, customers run AI close to their data and build use cases like personalization, fraud detection, and risk analytics.
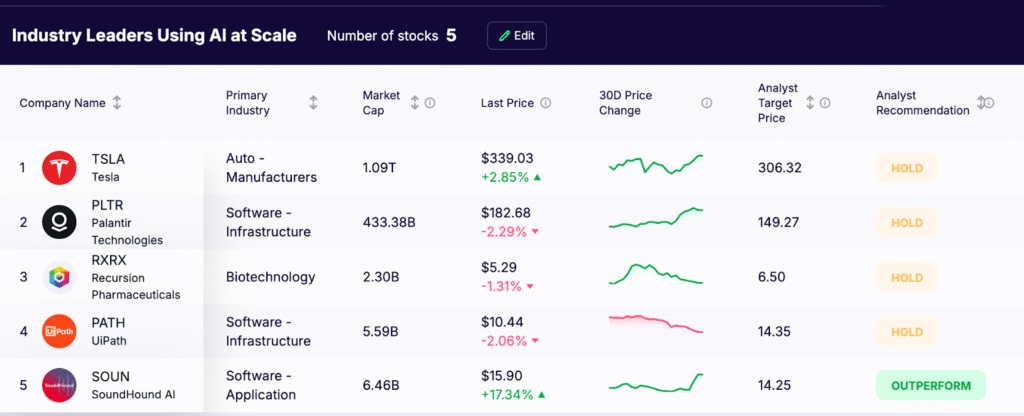
Industry Leaders Using AI at Scale
These companies apply AI directly to customer-facing products, transforming their industries.
- Tesla (TSLA): Develops Autopilot and Full Self-Driving using a camera-centric computer-vision stack trained on large volumes of fleet video. Runs intensive model training on company-owned infrastructure and deploys supervised driver-assist features where regulations permit.
- Palantir (PLTR): Provides the Gotham and Foundry platforms, plus AIP for AI-assisted workflows. Customers in government, defense, financial services, and healthcare use Palantir for secure data integration, analytics, and decision support.
- Recursion Pharmaceuticals (RXRX): Uses automated wet labs and high-content cellular imaging to build large biological datasets, then applies machine learning to discover and prioritize drug candidates. Partners with established pharma companies to move programs forward.
- UiPath (PATH): Offers an end-to-end automation platform that includes robotic process automation, process and task mining, and AI copilots. Enterprises use UiPath to reduce manual work, speed up back-office tasks, and integrate AI into existing workflows.
- SoundHound AI (SOUN): Delivers speech recognition and natural language understanding for voice assistants. Its technology powers in-car infotainment, restaurant ordering, and connected devices through software licensing and usage-based services.
Why These Stocks Are Relevant Now
AI 2.0 is reshaping valuations and how portfolios are built. Many leaders now sit in the trillion-dollar tier, and several have completed stock splits in recent years to improve liquidity and employee participation. Research services and professional screeners frequently flag these names for strong revenue and cash-flow growth, yet prices also embed high expectations. That makes entry discipline and position sizing critical.
The thesis extends beyond software into hard infrastructure. Enterprise digitization, e-commerce fulfillment, and autonomous systems in factories and warehouses are lifting demand for compute, storage, and connectivity. To build exposure with intent, track fundamentals and risk together:
- Revenue growth durability, gross margin trajectory, and free-cash-flow margin
- Capex intensity, return on invested capital, and time to ramp new capacity
- Contracted backlog and utilization of data center and GPU clusters
- Unit economics for AI workloads, including cost per token or inference
- Power procurement and cooling efficiency, which shape long-run margins
- Valuation vs growth, plus volatility-aware metrics like Sharpe and Sortino ratios, max drawdown, and downside capture
Compose positions across the stack. Blend hardware leaders, hyperscalers, and operators so one cycle buffers another. Use staged entries, set rebalance bands, and revisit allocations when growth slows, capital costs rise, or power constraints tighten. That approach can turn a fast-moving theme into a durable, compounding allocation.
The Takeaway for Investors
Investing in AI 2.0 means understanding the entire value chain. Compute starts with microscopic circuits and ends with assistants that sit inside everyday software. The leaders in this space design chips, build data centers, run cloud platforms, and deliver applications that customers pay for. These companies are shaping the next generation of business, healthcare, transportation, and entertainment.
Risk discipline is part of the thesis. Semiconductor supply chains face tariff and logistics sensitivity. Data privacy rules keep evolving. Power availability and cooling capacity can slow deployments. Portfolios tend to hold up better when exposure tilts toward firms with proven execution, strong balance sheets, secured power, and platforms that scale across multiple customers and use cases.
A simple playbook helps turn a theme into a plan. Define your mix across hardware, hyperscalers, and operators. Set entry ranges based on valuation and growth durability. Track capacity adds, contracted power, backlog, utilization, and free cash flow. Rebalance on schedule rather than on headlines. Use position sizing and risk metrics to keep outcomes aligned with your goals.
Momentum matters and so does durability. Leaders with repeat customer spend, deep partner ecosystems, and clear cost curves tend to compound over time. Focus on businesses that convert AI demand into revenue, margin, and cash generation.